Prostatitis is an inflammation of a person's prostate.The prostate is located under the bladder and the size of a chestnut.It surrounds the first part of the urethra and extends to the So pelvic floor composed of muscles.
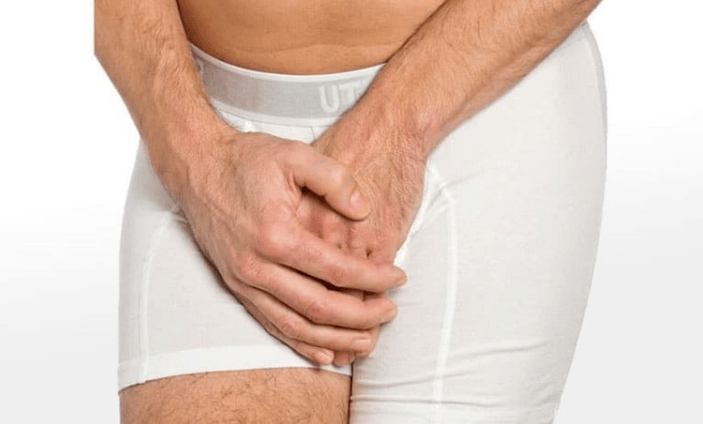
The prostate produces secretions, which include PSA and sperm.PSA makes ejaculation more fluid.Sperm is important for sperm mobility.
Prostatitis is mainly associated with severe pain in the perineum and anal areas.In addition, symptoms such as urination frequency, pain in the urine, and pain during ejaculation will occur during prostatitis.
The prostate is relatively frequently affected by inflammation.The possibility of prostate infection increases with age.Studies show that most cases are between 40 and 50 years old.
Prostatitis syndrome
At the same time, our understanding of the term prostatitis continues to expand.With SO called prostatitis syndrome, the human pelvic region summarizes several complaints, which are often unknown reasons.The term “prostatitis syndrome” summarizes various clinical paintings:
- Acute bacterial prostatitis
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis
- Inflammation and non-inflammatory syndrome of chronic pelvic pain
- Asymptomatic prostatitis
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is caused by bacteria.Bacteria either pass through the blood to the prostate or spread to the prostate from the bladder or urethra.Acute prostatitis is usually a serious general condition and is severely painful during urination, fever and chills.
Chronic prostatitis can develop from acute development: If more than three months, prostatitis and repeated microbial inflammation in the urine, SO is called prostate expression or ejaculation, then this is chronic inflammation.
Bacterial prostatitis.This is less than acute prostatitis.Although chronic inflammation of the prostate can cause pain during urination and may be a feeling of perineal stress, complaints are usually not expressed as in acute prostatitis.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (lipoprostatitis)
In most cases, bacteria cannot be detected in the urine, and the prostate or ejaculation is the cause of the disease.The triggers of prostatitis are not yet known.Doctors call it chronic pelvic pain.
However, in this case, white blood cells are usually detected as expression of inflammation in the prostate.To distinguish this, another form of bacteria and leukocytes has not been detected.Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is the most common form of prostatitis.
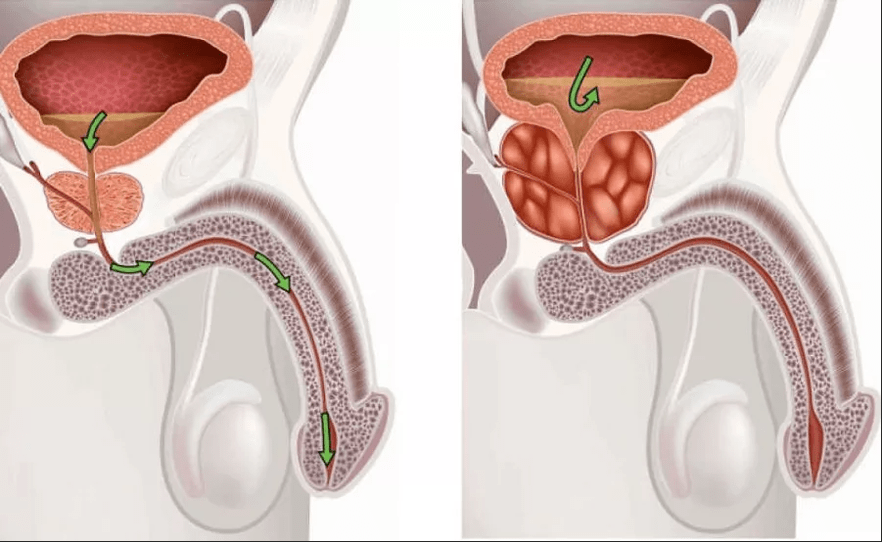
Asymptomatic prostatitis
In rare cases, asymptomatic prostatitis occurs.Despite this form of prostatitis, there are signs of inflammation, but no pain or other symptoms.For example, asymptomatic prostatitis is often detected by chance, for example, as part of an infertility study.
Prostatitis: Symptoms
Inflammation of the prostate can cause various symptoms of prostatitis.Although the symptoms of acute prostatitis can be very severe and can cause a strong discomfort, they are usually weaker due to chronic prostatitis.
Acute prostatitis: Symptoms
Acute prostatitis is usually an acute disease, and patients suffer from fever and chills.Urination can cause pain, and the flow of urine is significantly reduced due to prostate edema.Since victims can only distinguish between small amounts of urine, they have constant urination frequency and should usually go to the toilet.Other symptoms of prostatitis include bladder, pelvic pain, and back pain.Pain may also occur during or after ejaculation.
Chronic prostatitis: Symptoms
Prostatitis with a chronic course usually causes severe symptoms compared to acute inflammation of the prostate.Symptoms such as fever and cold are usually absent at all.Symptoms, such as the sensation of pressure in the perineum or lower abdomen, are typical for chronic inflammation of the prostate due to darkening of ejaculation from blood in sperm or blood in urine.There is no difference in symptoms of chronic bacteria and chronic obesity prostatitis.
Complications of prostatitis
The most common complication is a prostate abscess.Abscesses of the prostate are inflammatory purulent inflammation that usually require opening and emptying with a cut.
As a further complication of prostatitis, inflammation can be applied to nearby structures, such as testicles or testicle attachments.It is also suspected that chronic prostatitis is related to the development of prostate cancer.
Prostatitis: Causes and Risk Factors
Bacterial prostatitis: Cause
Only 10% of cases of prostatitis caused by prostate bacteria.Bacteria can enter the prostate through the blood or adjacent organs, such as the bladder or urethra, where they can cause an inflammatory response.
Escherichia coli bacteria are mainly found in the human intestine and are the most common cause of prostatitis.Klebsiella, enterococci or mycobacteria can also cause prostatitis.Bacterial prostatitis can also be caused by sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia or trichomonas infections as well as gonorrhea.
In chronic prostatitis, bacteria in the prostate avoid unclearable methods to protect the human immune system.This keeps microorganisms settled in the prostate.Antibiotics are relatively poor in prostate tissue, which may be another reason why bacteria survive in the prostate.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Causes
The exact cause of chronic pelvic pain syndrome has not been fully studied.Scientists nominate many theories, each sounds reasonable, but all of them have not been clearly proven.In some cases, genetic material from previously unknown microorganisms is found in the pelvis.Therefore, the cause of pelvic pain syndrome may be microorganisms that are still unable to be cultured in the laboratory and are therefore not detected.
Another possible cause of chronic pelvic pain is bladder disease.Due to impaired drainage, the volume of the bladder increases and hence presses on the prostate.This stress can eventually damage the tissues of the prostate, causing inflammation.
However, in many cases, the causes of chronic pelvic pain cannot be clearly demonstrated.Then, the doctor talks about idiopathic prostatitis.
Anatomical reasons
In rare cases, prostatitis is caused by narrowing the urinary tract.If the urinary tract is narrow, urine will accumulate and enter the prostate, which can also cause inflammation.This stenosis may be caused by a tumor or so-called prostate stones.
Psychological reasons
Recently, more and more psychological reasons have been discussed.In particular, non-inflammatory syndromes due to chronic pelvic pain may be a psychological trigger.The exact mechanism is still unknown.
Risk factors for the development of prostatitis
Some men are especially at risk of developing prostate infection.For example, these include men with immune system violations or immune system suppression.In addition, major diseases such as diabetes can lead to the development of prostatitis: Increased blood sugar levels in diabetics usually lead to increased levels of sugar in urine.The large amount of sugar in the urine can provide bacteria with good growth conditions, thereby promoting the development of urinary tract infection.
Another risk factor for the development of prostatitis is the binding of the bladder.A small rupture introduced into the urethra through the urethra through the urethra and damages the prostate.Additionally, like any foreign body, bacteria can precipitate on the bladder and form what SO is called a biofilm.As a result, bacteria can rise along the urethra to the bladder and cause prostate infection.
Prostatitis: Examination and diagnosis
A GP can use a medical history, but if prostatitis is suspected, he will direct you to a urologist.This performs a physical examination.If prostatitis is suspected, this is usually what So calls digital rectal study.However, this study did not provide clear evidence of prostate inflammation, but only confirmed suspicion.To detect bacterial prostatitis, laboratory tests can be performed
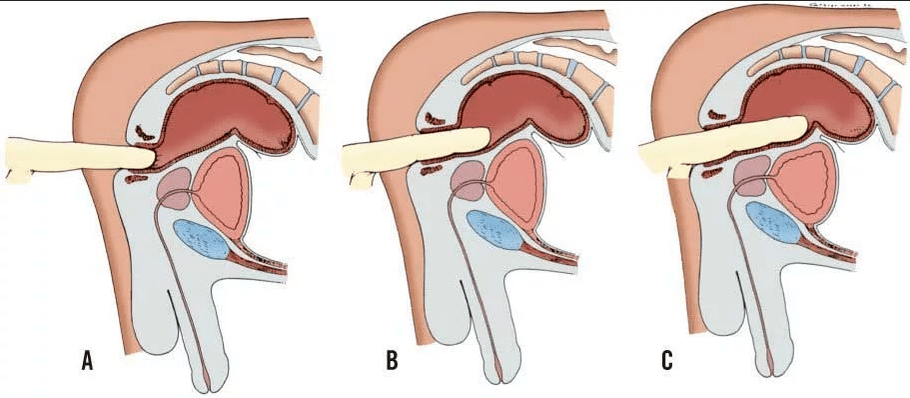
Finger rectal examination
Since the prostate directly borders the rectum, it can be palpated in the rectum.This digital rectal study was performed in an outpatient clinic and without anesthesia, usually painless.The patient is asked to lie down his legs.The doctor then uses lubricant, slowly inserts his finger into the anus and scans the prostate and adjacent organs.He examined the size and sensitivity of prostate pain.
Laboratory inspection
To identify possible pathogens, in most cases, urine analysis was performed.The standard method is a SO sample of four glasses.Erturin, Mittelstrahlurin, Prostataexprimat and Urin were tested after prostate massage.As Prostataxprimat said, doctors call it the secretion of the prostate.This is achieved by a doctor through light pressure on the prostate, for example, palpation.Pathogenic microorganisms and signs of inflammation can also be tested for ejaculation.
Further research
Ultrasound scans of the rectum can be used to determine the location and spread of inflammation.An important goal of the study is to rule out other diseases with similar symptoms.
To rule out that existing urine loss is caused by urethral stenosis, urine flow was measured.The normal flow of urine is 15 ml to 50 ml per second, while the flow of urine is 10 ml per second, and the obstructions in the urethra are high.
Prostatitis: Treatment

Drug Therapy
Acute bacterial prostatitis is treated with antibiotics.In mild cases, the dose of antibiotics is sufficient to last for ten days.In chronic prostatitis, this medication should be taken for a long time.Depending on the pathogenic microorganism, active substances of formicin, ciprofloxacin, azithromycin, erythromycin or doxycycline are suitable.Even if the symptoms have been relieved, in any case, antibiotics should be performed as appointed doctors.
Similarly, asymptomatic prostatitis is also treated with antibiotics.
Antibacterial treatment is usually ineffective if you have chronic catalytic prostatitis.Due to the lack of evidence of pathogens, an inflammatory syndrome of chronic pelvic pain was performed using antibiotics because it can sometimes improve.However, antibiotic therapy is not recommended for non-inflammatory syndromes with chronic pelvic pain.
Other therapeutic approaches are so-called 5α-reductase inhibitors such as solid acid ester or uramine, pentose disulfates and phyto-based drugs such as quercetin or dust extract.If no improvement is achieved, medication will be supplemented.Here, physical therapy exercises, exercises of the pelvic floor muscles or regular massage of the prostate are recommended.
In addition, symptom therapy can help alleviate the acute symptoms of prostate infection.Anesthetics can be prescribed for severe pain.Similarly, heating pads and heating pads on the back or lower abdomen help relax muscles.This usually relieves pain due to prostatitis.
relapse
The frequency of recurrence of prostatitis is usually very high.About 23% of victims suffered a second disease after one disease, 14% had three cases, and even 20% had a disease.To reduce the risk of relapse, avoid wet clothing in prostatitis, hypothermia, or using air bubbles such as black tea or coffee.This reduces the risk of cystitis and therefore lowers prostatitis.However, you cannot use these methods to reliably prevent bacterial prostatitis.
The prognosis of prostatitis depends on the cause of inflammation on the one hand, while on the other hand, the correct treatment begins.
In acute bacterial prostatitis, treatment is done as soon as possible with antibiotic treatment, and the prognosis is usually good.Taking antibiotics, pathogens die, which usually prevents the transition to chronic prostatitis.
About 60% of all patients with acute prostatitis no longer suffer from symptoms within six months, and about 20% of patients suffer from chronic prostatitis.Treatment and prognosis are more difficult here.In many cases, periodic episodes of this disease occur, and these events may accompany patients for many years.
Chronic prostatitis usually requires the patient's patience.Often, long-distance courses can be a serious psychological burden.
Patients suffering should seek professional help because mental health conditions have a huge impact on the prediction of prostatitis.